Silverlightを触り始めて結構立つのですが、いまだにMVVMって何??状態な私です。どうにもしっくりこないのですよね。というわけで、勉強のために簡単なSilverlight4アプリをポトペタで作り、それを徐々にMVVMらしくしていくことに挑戦してみました。
やたら長くなりましたが表記するコードをどう削れば良いかわからなかったことが原因なので、さらっと読めると思います。
目次
1. アプリの機能
こんな感じのSilverlight4アプリを作ってみます。
- 体重と身長を入力して計算ボタンを押すと、BMIを計算する
- 計算結果は履歴としてリストに保持する。
- 体重と身長が入力されていないときに計算ボタンが押されると、警告ダイアログを表示する。
2. とりあえず動くようにする(Viewのみで実装)
まずは、MVVMとか意識せずに素直に動くものを作ってみます。

MainPage.xamlです。
<UserControl x:Class="MVVMSample1.MainPage" xmlns:sdk="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation/sdk" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008" xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006" mc:Ignorable="d" d:DesignHeight="300" d:DesignWidth="400"> <Grid x:Name="LayoutRoot" Background="White"> <Grid.ColumnDefinitions> <ColumnDefinition Width="Auto"/> <ColumnDefinition Width="*"/> </Grid.ColumnDefinitions> <Grid.RowDefinitions> <RowDefinition Height="Auto"/> <RowDefinition Height="Auto"/> <RowDefinition Height="Auto"/> <RowDefinition Height="*"/> </Grid.RowDefinitions> <StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal" Margin="5"> <TextBlock Text="身長" VerticalAlignment="Center" Width="30"/> <TextBox x:Name="HeightTextBox" Width="150"/> <TextBlock Text="cm" VerticalAlignment="Center" Margin="5,0"/> </StackPanel> <StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal" Grid.Row="1" Margin="5"> <TextBlock Text="体重" VerticalAlignment="Center" Width="30"/> <TextBox x:Name="WeightTextBox" Width="150" /> <TextBlock Text="kg" VerticalAlignment="Center" Margin="5,0"/> </StackPanel> <Button x:Name="CalcButton" Content="計算" Grid.Row="2" Margin="5"/> <ListBox x:Name="RecordListBox" Grid.ColumnSpan="2" Grid.Row="3"> <ListBox.ItemTemplate> <DataTemplate> <StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal"> <TextBlock Text="{Binding DateTime}" VerticalAlignment="Center" /> <TextBlock Text=" : BMI = " VerticalAlignment="Center" /> <TextBlock Text="{Binding BMI}" VerticalAlignment="Center" /> </StackPanel> </DataTemplate> </ListBox.ItemTemplate> </ListBox> </Grid> </UserControl>
MainPage.xaml.csです。
public partial class MainPage : UserControl { private ObservableCollection<BMIRecord> bmiRecords = new ObservableCollection<BMIRecord>(); private int id = 0; public MainPage() { InitializeComponent(); this.RecordListBox.ItemsSource = this.bmiRecords; this.CalcButton.Click += this.CalcButton_Click; } private void CalcButton_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { // 身長を取得 double cmHeight; if (!double.TryParse(this.HeightTextBox.Text, out cmHeight)) { // 数値以外が入力されていた場合、メッセージを表示して何もしない。 MessageBox.Show("身長には数値を入力してください。"); return; } else if (cmHeight <= 0) { // 0または負の値が入力されていた場合、メッセージを表示して何もしない。 MessageBox.Show("身長には正の数を入力してください。"); return; } // 体重を取得 double weight; if (!double.TryParse(this.WeightTextBox.Text, out weight)) { // 数値以外が入力されていた場合、メッセージを表示して何もしない。 MessageBox.Show("体重には数値を入力してください。"); return; } else if (weight <= 0) { // 0または負の値が入力されていた場合、メッセージを表示して何もしない。 MessageBox.Show("体重には正の数を入力してください。"); return; } // BMIを計算 double mHeight = cmHeight / 100; double bmi = weight / (mHeight * mHeight); // BMIRecordクラスを生成 var record = new BMIRecord(); record.ID = this.id++; record.DateTime = DateTime.Now; record.Height = cmHeight; record.Weight = weight; record.BMI = bmi; // データグリッドに追加 this.bmiRecords.Add(record); } }
最後にリストボックスにセットするアイテムクラスです。
public class BMIRecord { /// <summary> /// ユニークなID /// </summary> public int ID { get; set; } /// <summary> /// 記録した日時 /// </summary> public DateTime DateTime { get; set; } /// <summary> /// 体重(kg) /// </summary> public double Weight { get; set; } /// <summary> /// 身長(cm) /// </summary> public double Height { get; set; } /// <summary> /// BMI値 /// </summary> public double BMI { get; set; } }
この段階では、MVVMも何もあったものじゃないですが、とりあえず要件どおりに動くアプリが完成しました。
3. ビジネスロジックの分離(Modelを導入)
ViewのみのコードからModelを分離してみましょう。今回の例ではBMIの計算処理と計算結果の履歴管理をモデルとして分離してみました。XAMLは前回と変わっていません。

MainPage.xaml.csはこう変わりました。
public partial class MainPage : UserControl { // モデルを保持する。 private MainModel model = new MainModel(); public MainPage() { InitializeComponent(); // モデルのRecordsプロパティをリストボックスにセットする。 this.RecordListBox.ItemsSource = this.model.Records; this.CalcButton.Click += this.CalcButton_Click; } private void CalcButton_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { // 身長を取得 double cmHeight; if (!double.TryParse(this.HeightTextBox.Text, out cmHeight)) { // 数値以外が入力されていた場合、メッセージを表示して何もしない。 MessageBox.Show("身長には数値を入力してください。"); return; } else if (cmHeight <= 0) { // 0または負の値が入力されていた場合、メッセージを表示して何もしない。 MessageBox.Show("身長には正の数を入力してください。"); return; } // 体重を取得 double weight; if (!double.TryParse(this.WeightTextBox.Text, out weight)) { // 数値以外が入力されていた場合、メッセージを表示して何もしない。 MessageBox.Show("体重には数値を入力してください。"); return; } else if (weight <= 0) { // 0または負の値が入力されていた場合、メッセージを表示して何もしない。 MessageBox.Show("体重には正の数を入力してください。"); return; } this.model.AddRecord(cmHeight, weight); } }
追加したModelです。
/// <summary> /// MainPageのModel。BMIの計算結果を管理する。 /// </summary> public class MainModel { private int id = 0; public MainModel() { this.Records = new ObservableCollection<BMIRecord>(); } /// <summary> /// BMI計算結果の履歴を取得する。 /// </summary> public ObservableCollection<BMIRecord> Records { get; private set; } /// <summary> /// BMIRecordをItemsSourceに追加する。 /// </summary> /// <param name="height"></param> /// <param name="weight"></param> public void AddRecord(double height, double weight) { var record = this.CreateRecord(height, weight); this.Records.Add(record); } /// <summary> /// BMIRecordクラスを生成する。 /// </summary> /// <param name="height"></param> /// <param name="weight"></param> /// <returns></returns> private BMIRecord CreateRecord(double height, double weight) { // BMIを計算 double mHeight = height / 100; double bmi = weight / (mHeight * mHeight); // BMIRecordクラスを生成 var record = new BMIRecord(); record.ID = this.id++; record.DateTime = DateTime.Now; record.Height = height; record.Weight = weight; record.BMI = bmi; return record; } }
4. バリデートエラー時にコントロールを赤くする(ViewModelを導入)
モデルとビューを分離したところで、バリデーションエラー時にコントロールが赤くなる機能を追加してみます。

バリデーション機能は、SilverlightのINotifyDataErrorInfo+DataAnnotationsを使いました。その結果クラス構成は以下のようになりました。

コードビハインドです。MainViewModelを保持し、バリデート処理をMainViewModelクラスに委譲するようにしました。
public partial class MainPage : UserControl { private MainViewModel viewModel = new MainViewModel(); private MainModel model = new MainModel(); public MainPage() { InitializeComponent(); this.DataContext = this.viewModel; this.RecordListBox.ItemsSource = this.model.Records; this.CalcButton.Click += this.CalcButton_Click; } private void CalcButton_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { // 値が入力されているかチェックする IEnumerable<string> errMessages = this.viewModel.Validate(); if (errMessages.Count() == 0) { // BMIを履歴に追加する。 double cmHeight = double.Parse(this.viewModel.HeightTextBox_Text); double weight = double.Parse(this.viewModel.WeightTextBox_Text); this.model.AddRecord(cmHeight, weight); } else { // エラーメッセージを表示する。 string msg = string.Join(Environment.NewLine, errMessages); MessageBox.Show(msg); } } }
ViewModelBaseクラスは、INotifyDataErrorInfo+DataAnnotationsとINotifyPropertyChangedの処理を受け持つクラスです。ほぼ下記のページのソースを流用させていただきました。
public class ViewModelBase : INotifyPropertyChanged, INotifyDataErrorInfo { public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged; public event EventHandler<DataErrorsChangedEventArgs> ErrorsChanged; /// <summary> /// オブジェクトに検証エラーがあるかどうかを示す値を取得します。 /// </summary> public bool HasErrors { get { // バリデーションエラー中のプロパティがあるかを返す。 IEnumerable<string> errMsgs = this.Validate(); return errMsgs.Count() > 0; } } /// <summary> /// 指定されたプロパティの検証エラーを取得します。 /// </summary> /// <param name="propertyName"></param> /// <returns></returns> public IEnumerable GetErrors(string propertyName) { // プロパティを検証 PropertyInfo info = this.GetType().GetProperty(propertyName); List<string> errMsgs = this.ValidateProperty(info); if (errMsgs.Count == 0) { // エラーなしの場合はnullを返す。 return null; } else { // エラーメッセージを返す return errMsgs; } } /// <summary> /// ViewModelをバリデートする /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> public IEnumerable<string> Validate() { IEnumerable<string> result = new List<string>(); // ValidationAttributeが付与されているプロパティの情報を収集する。 IEnumerable<PropertyInfo> propertyInfos = this.GetType() .GetProperties() .Where(propertyInfo => this.HasValidationAttribute(propertyInfo)); foreach (var propertyInfo in propertyInfos) { // エラーの場合、戻り値にマージ List<string> msgs = this.ValidateProperty(propertyInfo); result = result.Union(msgs); } return result; } /// <summary> /// PropertyChangedイベントを発行する。 /// </summary> /// <param name="propertyName"></param> protected void RaisePropertyChanged(string propertyName) { if (this.PropertyChanged != null) { var e = new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName); this.PropertyChanged(this, e); } } /// <summary> /// ErrorsChangedイベントを発行する。 /// </summary> /// <param name="propertyName"></param> protected void RaiseErrorsChanged(string propertyName) { if (this.ErrorsChanged != null) { var e = new DataErrorsChangedEventArgs(propertyName); this.ErrorsChanged(this, e); } } /// <summary> /// ValidationAttributeが付与されているかを判定する。 /// </summary> /// <param name="pi"></param> /// <returns></returns> private bool HasValidationAttribute(PropertyInfo pi) { return pi.CanRead && pi.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(ValidationAttribute), false).Length > 0; } /// <summary> /// プロパティをバリデートする。 /// </summary> /// <param name="info"></param> /// <returns></returns> private List<string> ValidateProperty(PropertyInfo info) { string propertyName = info.Name; object propertyValue = info.GetValue(this, null); var context = new ValidationContext(this, null, null); context.MemberName = propertyName; var results = new List<ValidationResult>(); if (!Validator.TryValidateProperty(propertyValue, context, results)) { // 文字列のリストに変換して返す。 return results.Select(vr => vr.ErrorMessage) .ToList(); } else { // エラーがない場合、空リストを返す。 return new List<string>(); } } }
最後にMainViewModelのコードです。このクラスには現状バインディングソースプロパティしかありません。
public class MainViewModel : ViewModelBase { private string heightTextBox_Text = string.Empty; private string weightTextBox_Text = string.Empty; [RegularExpression( @"^[0-9]+(\.)?[0-9]*$", ErrorMessage = "身長には正の数値を入力してください。")] [Required(ErrorMessage = "身長を入力してください")] public string HeightTextBox_Text { get { return this.heightTextBox_Text; } set { if (!Equals(this.heightTextBox_Text, value)) { this.heightTextBox_Text = value; this.RaisePropertyChanged("HeightTextBox_Text"); this.RaiseErrorsChanged("HeightTextBox_Text"); } } } [RegularExpression( @"^[0-9]+(\.)?[0-9]*$", ErrorMessage = "体重には正の数値を入力してください。")] [Required(ErrorMessage = "体重を入力してください")] public string WeightTextBox_Text { get { return this.weightTextBox_Text; } set { if (!Equals(this.weightTextBox_Text, value)) { this.weightTextBox_Text = value; this.RaisePropertyChanged("WeightTextBox_Text"); this.RaiseErrorsChanged("WeightTextBox_Text"); } } } }
5. インスタンス参照の見直し(V → VM → Mに)
前回のクラス構成では、ViewはViewModelから値を取得してモデルに渡していますが、これでは、ViewがModelを持っている意味があまりありません。そこで、各クラスのインスタンス参照を整理しました。

MainViewModelクラスにAddRecordメソッドを追加し、MainPage.xaml.csはこのメソッド呼ぶように変更しました。
/// <summary> /// BMIRecordを履歴に追加する。 /// </summary> public void AddRecord() { double cmHeight = double.Parse(this.HeightTextBox_Text); double weight = double.Parse(this.WeightTextBox_Text); this.model.AddRecord(cmHeight, weight); }
やっとMVVMの構成ぽくなりましたね。
6. Xaml.csのコードをVMへ移行(コマンドを導入)
前回までの状態ですと、MainPage.xaml.csにはイベントハンドラを書くためだけに存在しているような状態です。そこで、コードビハインドに記述された処理をコマンドを使って移行してみます。Silverlightでコマンドを実装するのはしんどいので、Prismを使いました。
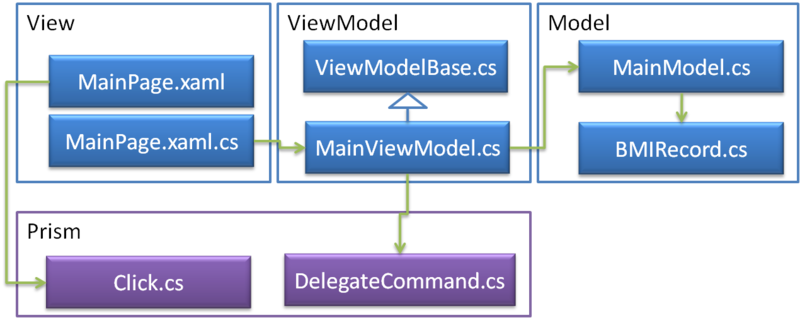
なお、今回使用したDllは以下の通りです。
- Microsoft.Practices.Prism.dll
Xamlの計算ボタンにコマンドのバインド設定をします。
<Button x:Name="CalcButton" Content="計算" prism:Click.Command="{Binding AddRecordCommand}" Grid.Row="2" Margin="5"/>
MainPage.xaml.csです。DataContextへVMを設定する以外の処理がなくなりました。
public partial class MainPage : UserControl { public MainPage() { InitializeComponent(); this.DataContext = new MainViewModel(); } }
MainViewModelにDelegateCommandを定義します。
public class MainViewModel : ViewModelBase { private DelegateCommand addRecordCommand; private string heightTextBox_Text = string.Empty; private string weightTextBox_Text = string.Empty; private MainModel model = new MainModel(); public MainViewModel() { this.addRecordCommand = new DelegateCommand(this.AddRecord); } /// <summary> /// 計算ボタンのクリックイベントに対応するコマンド /// </summary> public DelegateCommand AddRecordCommand { get { return this.addRecordCommand; } } [RegularExpression( @"^[0-9]+(\.)?[0-9]*$", ErrorMessage = "身長には正の数値を入力してください。")] [Required(ErrorMessage = "身長を入力してください")] public string HeightTextBox_Text { get { return this.heightTextBox_Text; } set { if (!Equals(this.heightTextBox_Text, value)) { this.heightTextBox_Text = value; this.RaisePropertyChanged("HeightTextBox_Text"); this.RaiseErrorsChanged("HeightTextBox_Text"); } } } [RegularExpression( @"^[0-9]+(\.)?[0-9]*$", ErrorMessage = "体重には正の数値を入力してください。")] [Required(ErrorMessage = "体重を入力してください")] public string WeightTextBox_Text { get { return this.weightTextBox_Text; } set { if (!Equals(this.weightTextBox_Text, value)) { this.weightTextBox_Text = value; this.RaisePropertyChanged("WeightTextBox_Text"); this.RaiseErrorsChanged("WeightTextBox_Text"); } } } public ObservableCollection<BMIRecord> Records { get { return this.model.Records; } } /// <summary> /// BMIRecordを履歴に追加する。 /// </summary> public void AddRecord() { // 値が入力されているかチェックする IEnumerable<string> errMessages = this.Validate(); if (errMessages.Count() == 0) { // BMIを履歴に追加する。 double cmHeight = double.Parse(this.HeightTextBox_Text); double weight = double.Parse(this.WeightTextBox_Text); this.model.AddRecord(cmHeight, weight); } else { // エラーメッセージを表示する。 string msg = string.Join(Environment.NewLine, errMessages); MessageBox.Show(msg); } } }
7. ダイアログ表示処理をVへ戻す(VM → Vの操作)
これで完成!と思ったら、VMにVがやるべき処理を紛れ込ませてしまいました。バリデーションエラー時にダイアログを表示するこの処理のことです。
// エラーメッセージを表示する。 string msg = string.Join(Environment.NewLine, errMessages); MessageBox.Show(msg);
せっかく、VとVMとMで責務を分けたので、上記処理をViewに戻しましょう。VMからVを操作する方法は下記のページを参考にしました。
なお、今回使用したDllは以下の通りです。
- Microsoft.Practices.Prism.dll
- Microsoft.Practices.Prism.Interactivity.dll
- System.Windows.Interactivity.dll(Blend SDK)
まず、MainViewModelにInteractionRequestを定義します。こいつ経由でViewに通知を行うことになります。
public class MainViewModel : ViewModelBase { private InteractionRequest<Confirmation> alertRequest; private DelegateCommand addRecordCommand; private string heightTextBox_Text = string.Empty; private string weightTextBox_Text = string.Empty; private MainModel model = new MainModel(); public MainViewModel() { this.alertRequest = new InteractionRequest<Confirmation>(); this.addRecordCommand = new DelegateCommand(this.AddRecord); } public IInteractionRequest AlertRequest { get { return this.alertRequest; } } /// <summary> /// 計算ボタンのクリックイベントに対応するコマンド /// </summary> public DelegateCommand AddRecordCommand { get { return this.addRecordCommand; } } [RegularExpression( @"^[0-9]+(\.)?[0-9]*$", ErrorMessage = "身長には正の数値を入力してください。")] [Required(ErrorMessage = "身長を入力してください")] public string HeightTextBox_Text { get { return this.heightTextBox_Text; } set { if (!Equals(this.heightTextBox_Text, value)) { this.heightTextBox_Text = value; this.RaisePropertyChanged("HeightTextBox_Text"); this.RaiseErrorsChanged("HeightTextBox_Text"); } } } [RegularExpression( @"^[0-9]+(\.)?[0-9]*$", ErrorMessage = "体重には正の数値を入力してください。")] [Required(ErrorMessage = "体重を入力してください")] public string WeightTextBox_Text { get { return this.weightTextBox_Text; } set { if (!Equals(this.weightTextBox_Text, value)) { this.weightTextBox_Text = value; this.RaisePropertyChanged("WeightTextBox_Text"); this.RaiseErrorsChanged("WeightTextBox_Text"); } } } public ObservableCollection<BMIRecord> Records { get { return this.model.Records; } } /// <summary> /// BMIRecordを履歴に追加する。 /// </summary> public void AddRecord() { // 値が入力されているかチェックする IEnumerable<string> errMessages = this.Validate(); if (errMessages.Count() == 0) { // BMIを履歴に追加する。 double cmHeight = double.Parse(this.HeightTextBox_Text); double weight = double.Parse(this.WeightTextBox_Text); this.model.AddRecord(cmHeight, weight); } else { // Viewにエラーメッセージダイアログ表示リクエストを投げる var confirmation = new Confirmation(); confirmation.Title = "バリデーションエラー"; confirmation.Content = string.Join(Environment.NewLine, errMessages); ; alertRequest.Raise(confirmation); } } }
XAMLにVMからの通知を受け取るためにInteractionRequestTriggerにConfirmActionを設定します。ConfirmActionは、自作のActionです。
<UserControl x:Class="MVVMSample6.MainPage" xmlns:sdk="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation/sdk" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008" xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006" mc:Ignorable="d" xmlns:prism="http://www.codeplex.com/prism" xmlns:i="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/2010/interactivity" xmlns:myAction="clr-namespace:MVVMSample6" d:DesignHeight="300" d:DesignWidth="400"> <Grid x:Name="LayoutRoot" Background="White"> <Grid.ColumnDefinitions> <ColumnDefinition Width="Auto"/> <ColumnDefinition Width="*"/> </Grid.ColumnDefinitions> <Grid.RowDefinitions> <RowDefinition Height="Auto"/> <RowDefinition Height="Auto"/> <RowDefinition Height="Auto"/> <RowDefinition Height="*"/> </Grid.RowDefinitions> <i:Interaction.Triggers> <!-- アラートウィンドウを出すためのTriggerAction --> <prism:InteractionRequestTrigger SourceObject="{Binding AlertRequest, Mode=OneWay}"> <myAction:ConfirmAction/> </prism:InteractionRequestTrigger> </i:Interaction.Triggers> <StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal" Margin="5"> <TextBlock Text="身長" VerticalAlignment="Center" Width="30"/> <TextBox x:Name="HeightTextBox" Text="{Binding HeightTextBox_Text, Mode=TwoWay}" Width="150"/> <TextBlock Text="cm" VerticalAlignment="Center" Margin="5,0"/> </StackPanel> <StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal" Grid.Row="1" Margin="5"> <TextBlock Text="体重" VerticalAlignment="Center" Width="30"/> <TextBox x:Name="WeightTextBox" Text="{Binding WeightTextBox_Text, Mode=TwoWay}" Width="150" /> <TextBlock Text="kg" VerticalAlignment="Center" Margin="5,0"/> </StackPanel> <Button x:Name="CalcButton" Content="計算" prism:Click.Command="{Binding AddRecordCommand}" Grid.Row="2" Margin="5"/> <ListBox x:Name="RecordListBox" ItemsSource="{Binding Records}" Grid.ColumnSpan="2" Grid.Row="3"> <ListBox.ItemTemplate> <DataTemplate> <StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal"> <TextBlock Text="{Binding DateTime}" VerticalAlignment="Center" /> <TextBlock Text=" : BMI = " VerticalAlignment="Center" /> <TextBlock Text="{Binding BMI}" VerticalAlignment="Center" /> </StackPanel> </DataTemplate> </ListBox.ItemTemplate> </ListBox> </Grid> </UserControl>
最後にメッセージボックスを表示するConfirmActionを定義します。
public class ConfirmAction : TriggerAction<DependencyObject> { protected override void Invoke(object parameter) { // イベント引数とContextを取得する var args = parameter as InteractionRequestedEventArgs; var confirmation = args.Context as Confirmation; // MessageBoxを表示する。 MessageBox.Show( confirmation.Content as string, confirmation.Title as string, MessageBoxButton.OK); } }
8. まとめ
だらだらとMVVMへと変化させる様子を書いてみたのですが、いかがだったでしょうか?ちなみに私は、コマンドをまともに使ったことがありません。「5. インスタンス参照の見直し(V → VM → Mに)」の段階のクラス構成を好んで使います。
私がコマンドを使わないのは、
- 少人数で開発することが多い。
- コマンドを定義するのが面倒くさい
- というかイベントハンドラ大好き
あたりが理由なんだと思います。
大人数でたくさんの画面を手分けして作るようなプロジェクトですと、コードの均一化のためにコマンドを使うのはありなのかもしれません。なぜコマンドが推奨されているか理解するためには、もうちょっと勉強が必要だな、と思いました。
